If you’re running a manufacturing plant, you know the daily challenges all too well: machines breaking down without warning, production lines slowing down, inconsistent product quality, and the constant pressure to reduce costs and meet growing demand. It can feel like you’re always firefighting instead of focusing on growth.
That’s where industrial automation comes in. By integrating smart mechanical designs, PLCs, HMI dashboards, and simulation tools into your manufacturing line, you can make production more predictable and boost operational efficiency.
In this blog, we’ll break down exactly how automation can solve your toughest manufacturing challenges. You’ll also learn what to look for when choosing the right industrial automation solutions for your business so you can make confident decisions that deliver real results. Keep reading.
What is Industrial Automation in Manufacturing?
Automation in manufacturing is the use of machines, control systems, and software to perform production tasks that would normally require human effort. It relies on technologies like PLCs, HMIs, robotics, and simulation tools to run processes like assembly, picking, sorting, welding, packaging, and quality checks with minimal manual intervention.
At its core, manufacturing automation is about improving efficiency, reducing errors, and making production processes more predictable and scalable.
What are Automated Manufacturing Systems?
While industrial automation explains the idea, automated manufacturing systems are the practical setups you see on the factory floor. These systems bring together machines, PLCs, sensors, robotics, and material-handling equipment into one coordinated flow. Instead of operators handling each step, the system moves parts, assembles components, handles hazardous tasks and runs quality checks automatically.
The real value comes from how seamlessly these pieces work together to keep production running 24/7 while freeing people to focus on higher-value work.
Why Do Manufacturers Need Automation?
If you’ve ever dealt with a stalled manufacturing line or products that didn’t meet quality standards, you already know why automation is essential. Manufacturers today face pressures that simply can’t be solved by putting more people to work.
Here are some of the biggest reasons factories are turning to manufacturing automation:
- Unplanned downtime affects profits: Machines fail without warning, and every hour lost means missed deadlines and wasted money.
- Manual processes lead to errors: Even the best-trained operators can make mistakes, especially when tasks are repetitive. Automation ensures consistency and keeps products at top quality.
- Labor shortages and rising costs: Skilled technicians are harder to find and more expensive to retain. Automated manufacturing systems reduce reliance on manual labor for repetitive work.
- Hazardous and repetitive work puts people at risk: Some tasks like heavy lifting, welding, and handling hot materials, are risky and exhausting. Automation takes on these tough tasks, keeping your team safe and the manufacturing line steady. It not only protects workers but also helps you meet safety standards and avoid costly accidents.
- Scaling up is hard without smart systems: Meeting growing demand with the same setup is tough. Automation makes it possible to expand production without proportionally increasing costs.
- Customers expect better quality, faster delivery: In today’s market, mistakes or delays can mean losing valuable contracts. Automation helps you stay precise and on schedule.
How Does Automation Improve Manufacturing Efficiency?
Once you decide to adopt automation, the real benefits start to show on the manufacturing floor.
Here’s how it works in practice:
Smarter Machine & Process Design
Automation begins with designing machines and production processes to work smoothly together. By eliminating bottlenecks, reducing waste, and keeping materials moving efficiently, every step of manufacturing becomes more predictable and reliable.
This kind of thoughtful design ensures faster production, fewer interruptions, and overall, more efficient operations.
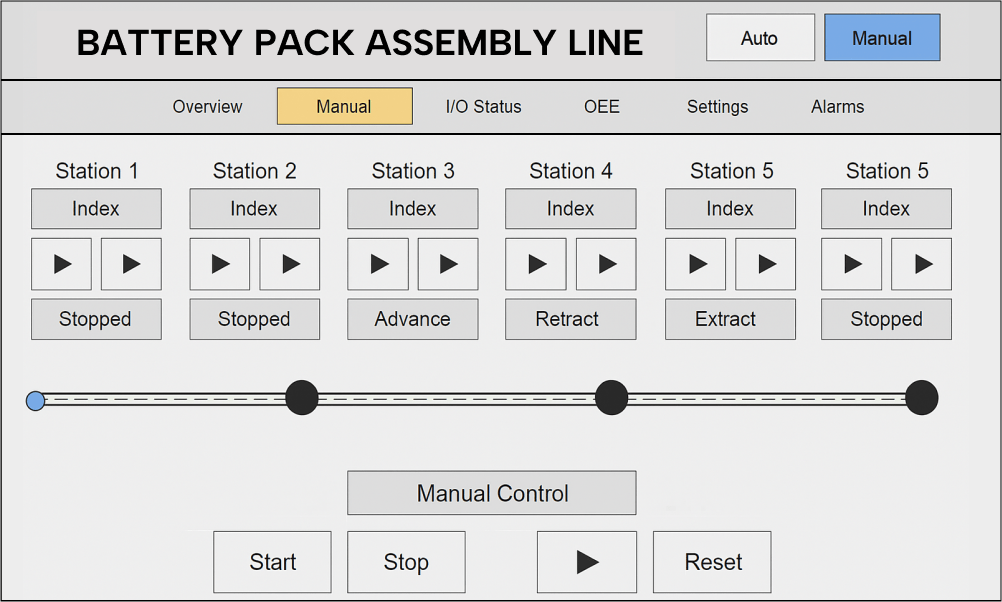
Intelligent Controls (PLCs, HMIs, SCADA)
Instead of relying on operators to constantly manage machines, programmable logic controllers (PLCs) handle processes in real time, adjusting speed, monitoring quality, and even shutting down safely if something goes wrong.
With easy-to-use HMI dashboards, operators can see exactly what’s happening on the floor. They can make quick adjustments and fix issues before they turn into downtime. This real-time control gives teams better visibility, improves efficiency, and reduces errors.
Simulation & Digital Twins
Some of the biggest gains in efficiency happen even before a machine is even switched on. With robotic simulation, manufacturers can test workflows virtually, spot bottlenecks, and refine processes before they hit the factory floor. This prevents costly trial-and-error and ensures new systems perform as expected from day one.
For example, digital manufacturers who implement automation can see 30–50% reductions in machine downtime, 10–30% increases in throughput, and 15–30% improvements in labor productivity (McKinsey).
Examples of Automated Systems in Manufacturing
Modern factories use automated systems to make everyday manufacturing tasks easier, safer, and more reliable. These industrial automation applications handle everything from moving materials and assembling parts to checking quality. Let’s take a closer look at some real examples of how these systems work on the shop floor.
1. Robotic Welding Cells
Robotic welding cells are widely used in automotive, heavy equipment, and fabrication plants. They deliver consistent weld quality, reduce the risk of defects, and improve safety by keeping workers away from hazardous environments.
2. Automated Palletizing and Depalletizing
Automated palletizing systems handle the stacking and unstacking of products at the end of production lines. They help reduce manual lifting, minimize errors, and keep material handling fast and efficient.
3. Robotic Painting Systems
Robotic painting systems are common in automotive and appliance manufacturing. They apply coatings evenly, improve finish quality, and cut down on paint waste, which lowers production costs.
4. Automated Assembly Lines
Automated assembly lines use robotic arms and pick-and-place systems to complete repetitive tasks. They maintain accuracy across every unit and allow to increase output without sacrificing quality.
5. CNC Machining Centers
CNC machining centers are essential for precision cutting, drilling, and shaping in industries like aerospace and automotive. They make it possible to produce complex parts with accuracy and repeatability.
6. 3D Printing (Additive Manufacturing)
3D printing is used for rapid prototyping, tooling, and short production runs. It helps to test designs quickly and reduce the time and cost of traditional part development.
7. Vision Inspection Systems
Vision inspection systems use cameras and sensors to check parts for defects in real time. They help improve quality control and prevent costly rework or recalls.
8. Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS)
Automated storage and retrieval systems organize raw materials and finished products in warehouses. They save floor space, improve accuracy, and reduce the time needed to move materials in and out of storage.
9. PLC, HMI, and SCADA Systems
PLC, HMI, and SCADA systems form the control backbone of modern factories. They allow operators to monitor machines, adjust processes, and keep the line running smoothly from a single interface.
Which Manufacturing Industries Benefit the Most from Automation?
Automotive
Automation in automotive plants can efficiently handle tasks like welding, assembly, painting, and quality inspection. These systems help vehicle manufacturers handle high-volume production while keeping costs down and meeting strict safety and performance standards.
Aerospace
In aerospace, precision is non-negotiable. Automated CNC machining, drilling, and inspection systems allow manufacturers to produce complex parts with tight tolerances and maintain repeatability across production runs.
Electronics
Electronics manufacturing depends on automated assembly, soldering, and vision inspection systems. These applications improve product reliability, reduce human error, and keep up with the fast pace of consumer demand.
Food and Beverage
Automated packaging, palletizing, and inspection systems keep food and beverage manufacturing consistent and compliant with hygiene standards. They help scale output without sacrificing quality.
Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices
In the pharma industry, automation ensures accurate dosing, sterile handling, and secure packaging. These systems reduce the risk of contamination and help manufacturers meet strict regulatory requirements.
Heavy Equipment and Industrial Machinery
Manufacturers of heavy equipment and machinery use robotic welding, CNC machining, and automated material handling to build large, complex assemblies. Automation improves safety, shortens production cycles, and reduces labor costs.
The ROI of Automation in Manufacturing Industry
Despite its clear benefits, the biggest hesitation manufacturers have about automation is the upfront cost. Robots, PLCs, and automated equipment can look like heavy capital expenses. The real question is: will this investment pay off?
The answer is clear. While automation may feel like a big investment at first, the benefits quickly outweigh the costs. Automation can cut labor expenses by up to 40%, while also cutting errors that lead to waste, downtime, and rework.
Moreover, predictive controls keep machines running smoothly, lowering unplanned stoppages and extending equipment life.
That’s why most automation projects recover their investment within 12–24 months. Many even deliver 150%+ ROI over time. Also, manufacturers can cut unplanned downtime by up to 50%, while throughput and output often increase 25–50% (IoTMag, Quintec).
In fast-moving markets, this ROI helps you stay competitive, scale efficiently, and keep your manufacturing line running smoothly.
Choosing the Right Automation Partner
For many manufacturers, the biggest challenge is not deciding whether to automate but figuring out how to do it effectively. Every plant is different, and solutions that work in one facility may not be the right fit for another. That is where the right manufacturing automation partner makes all the difference.
At Sedin Engineering, we work closely with manufacturers to design and deliver industrial automation services tailored to their manufacturing line. Our solutions include:
- Mechanical Design – Developing robust and efficient machine designs that improve performance and reliability.
- Controls Engineering – Designing PLC, HMI, and SCADA systems that give manufacturers real-time control over their processes.
- PLC Programming and Integration – Configuring automation logic to ensure machines and production lines run smoothly together.
- Simulation and Virtual Commissioning – Testing and validating systems digitally before they go live, which reduces downtime and speeds up implementation.
By combining these capabilities, we help manufacturers reduce risk, accelerate ROI, and create automation systems that are built to grow with their business. Contact us today to see how we can make your manufacturing line smarter and more profitable.