Industrial automation is rapidly becoming essential across industries like manufacturing, food and beverage, power generation and construction. For manufacturers especially, automation means one thing: more productivity with lower costs. And in today’s competitive market, that can make all the difference.
What’s driving this rapid change? Industry 4.0 technologies like big data, cloud computing, artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) are transforming how factories run. These smart tools help manufacturers work faster, smarter and more flexibly — setting the stage for the next wave of industrial innovation.
In this blog, we’ll take you through the fundamentals of industrial automation. You’ll learn about the key technologies shaping the industry and discover practical ways automation can help your business cut waste and stay ahead of the competition.
Ready to see how automation can power your manufacturing success? Let’s dive in.
What is Industrial Automation?
Industrial automation refers to the use of various tools and methods in industrial processes and machinery to minimize human intervention. With technologies like control systems and robotics, machines can perform tasks on their own without manual labor. This leads to reduced operational costs, minimized waste, improved quality, and enhanced overall efficiency.
Whether integrating automation into existing industrial processes or introducing a standalone system, automation boosts safety and productivity. It allows industries to meet their customer demands more quickly and efficiently — maximizing their return on investment (ROI).
Types of Industrial Automation
1. Fixed Automation
Fixed automation, also known as hard automation, is designed to perform specific tasks that need a consistent and high production rate. Once set up for a particular function, a fixed automation system is hard to reprogram for a different process.
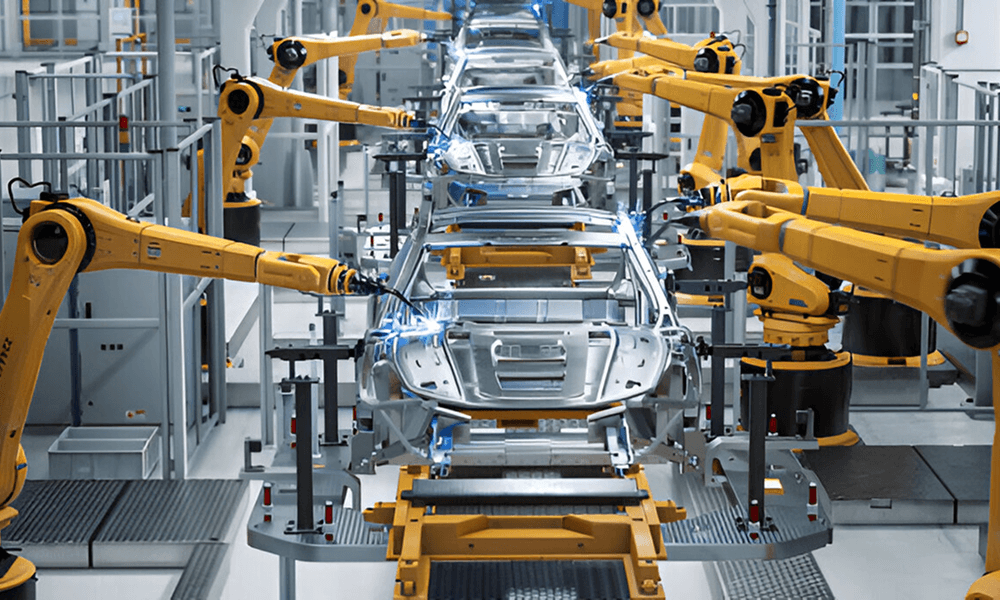
This type of automation is commonly used in industries that require mass production, like automotive assembly lines and food packaging facilities.
2. Programmable Automation
Unlike fixed automation systems, programmable automation allows the reprogramming of machines to adjust production parameters. This flexibility helps machines to perform tasks under varying production demands, like in the case of batch processing.
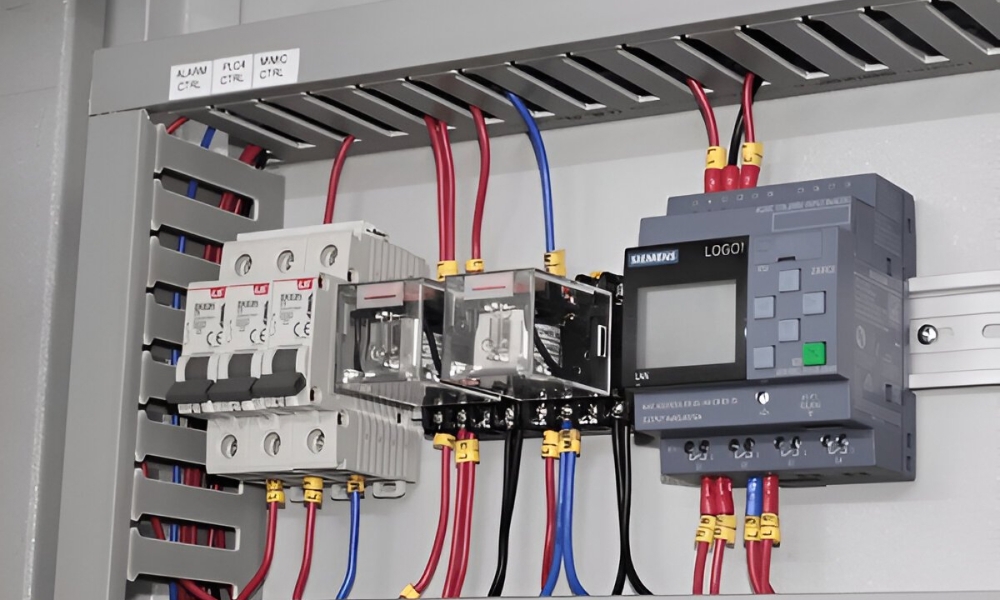
A key component of programmable automation is the Programmable Logic Controller (PLC), which facilitates the easy configuration and control of machinery for different tasks.
3. Flexible Automation
While programmable automation systems require significant time to reprogram for different product variants, flexible automation allows machines to adapt to various tasks and meet diverse production demands at a faster rate.
This type of automation is best suited for environments where products have short life cycles and require significant customization, like in the manufacturing of automotive body parts. Computerized Numerical Control (CNC) machines are commonly employed to achieve flexible automation.
4. Integrated Automation
Integrated automation system combines different processes, tools, and data to create a cohesive industrial workflow. This end-to-end automated manufacturing approach minimizes human intervention and offers a holistic strategy to maximize return on investment and reduce losses in industrial operations.
A perfect example of this is lights-out manufacturing, where fully automated systems carry out the entire production process without any human involvement in the manufacturing unit.
Industrial Automation Tools and Technologies
Several automation tools are used in various industries today, each offering unique features.
Programmable Logic Controller (PLC)
A PLC is a digital computer designed for industrial automation. It performs specific tasks in response to customized instructions, which are either automated data inputs or manually entered by an operator. A PLC is an example of a hard real-time system, which means it should produce results in response to given inputs within a limited time.
Process Control System (PCS)
A Process Control System (PCS) is a set of methodologies used to control industrial processes to ensure they operate within desired parameters. Usually, this system includes sensors that collect data like temperature and pressure and send signals to actuators to make necessary changes when required.
Distributed Control System (DCS)
This is a specific type of process control system where control elements are distributed throughout the system rather than being centralized. This setup enables real-time monitoring and control of various industrial operations across multiple locations. DCS is ideal for large and complex industrial processes that require precise control at several locations, like in electric power generation plants.
Human Machine Interface (HMI)
HMI is a user interface that facilitates interaction between a person and a machine or a process. HMI can be used to display real time data and performance metrics of any industrial process. It enables the operator to monitor inputs and outputs for optimized production process.
Robots
Robots are the machines that are programmed to perform a specific task with little or no human intervention. They can sense any change in their environment, make decisions and perform a series of actions automatically. Industrial robots are programmed to perform simple repetitive tasks to complex processes with high precision and efficiency.
Supervisory Control and Data Aquisition (SCADA)
SCADA is an advanced automation system, used to monitor and control industrial devices and processes. This system enables the collection of remote and on-site data for industrial equipment. SCADA offers a comprehensive view of overall system performance and helps in process management.
Top Benefits of Industrial Automation

1. Automation boosts productivity
Automation allows machines to handle repetitive tasks. By streamlining different processes, automation helps reduce cycle times and increase output. This results in faster production rates and increases the overall productivity of the manufacturing unit.
2. Automation improves efficiency
Automated processes mean less human intervention and fewer errors in routine tasks like reading labels. Automation supports industrial operations for longer periods without compromising the production quality. Plus, it enables operators to monitor the overall process without the need to focus on individual tasks, increasing the overall operational efficiency.
3. Industrial automation reduces costs
Automated industrial processes require minimal human involvement, reducing labor costs. Although the initial investment in automation may be higher, in high-production environments, overall operational expenses decrease significantly.
4. Safe manufacturing processes
Automated machines can replace human operators working in hazardous environments. This helps in reducing accidental risks and enhancing workplace safety. In the case of a hazardous situation, operators can monitor from a distance, allowing for quicker response and disaster recovery. Automated processes can also detect anomalies and predict machine failure.
5. High quality products
Real-time data logging and analysis enable manufacturers to easily identify process malfunctions or defects without disrupting the overall operation. This helps them quickly resolve the issues, leading to higher quality production.
Additionally, automated checks can determine if certain ingredients have lost their effectiveness over time, ensuring the quality of raw materials. This approach minimizes waste and enhances overall efficiency.
6. Automation helps in process optimization
Automated systems can easily integrate with data, enabling data-driven decision-making and improvements. For example, in inventory management, automation simplifies the recording of available stock and identifies product or material shortages by tracking inventory levels. Automation allows for real-time analytics, which helps in optimizing the entire process.
7. It is flexible and scalable
Automated industrial systems can be reprogrammed to meet varying production demands. Plus, these systems allow the collection of all production process-related data in one place. This enables employees to easily adhere to requirements and adapt to the workflow. Such industrial operations have more flexibility and scalability.
8. Regulation compliance is easier
Automated industrial processes can accurately track and record data. This real time monitoring helps industries to quickly identify and address compliance issues. Automation also makes control and documentation much easier, so regulation compliance gets easier.
Industrial Automation Applications
- Oil and gas
- Manufacturing
- Automotive assembly lines
- Special purpose machines
- Sonic/ultrasonic machines
- Testing and vision systems
- Welding applications
- Material handling
- Food and beverages
- Semiconductor control
Why Choose Sedin Engineering to Automate Your Business?
Industrial automation can help modernize your business processes and integrate emerging technologies for better production efficiency.
We, at Sedin Engineering, believe in doing it right the first time. Whether you want to integrate automation services into your existing industrial processes or implement it as a standalone system, we can help you achieve the most optimized solution that best fits your needs.
Our advanced tools ensure top-quality production and our design for manufacturing (DFM) techniques guarantee that processes are cost-effective and safe. We can assist you with:
- Conceptualizing the automation process
- Designing components for automation
- Developing high-quality HMIs for easy interaction
- Conducting robotic simulations
- Providing design validation
- Offering expert industrial automation consultation
And we ensure the end result is the best and adhere to the industry standards and clients' requirements.
Want to automate your production process? Contact Sedin’s industrial automation service experts to get customized solutions for your industry.