Keeping machines and plants running smoothly isn’t easy. Everything needs to move fast, stay safe and work without breaks. That’s where SCADA comes in.
SCADA stands for Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition. In industrial and manufacturing plants, it helps engineers and operators watch over equipment, collect data and control systems, all from one place.
If you build machines, manage projects or work on automation, SCADA can make your job easier. It saves time. It reduces errors. It gives you better control.
In this blog, we’ll explain what SCADA is, how it works and why it’s crucial for anyone involved in designing, developing or running industrial systems.
What is SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition)?
SCADA is a system that lets you monitor and control machines, equipment and industrial processes from a central location.
SCADA acts as the interface between you and your operation. It shows you what’s happening in real time on screens, dashboards and alarms. You can see if a motor is running, check tank levels or turn off a pump, all without walking to the machine.
A SCADA system connects to sensors, PLCs and other control devices. It collects data, displays it in a simple way and lets you take action when needed. It also stores data for reports and future analysis.
Whether it’s a factory, a water treatment plant or a power station, SCADA systems help you run things better, faster and safer.
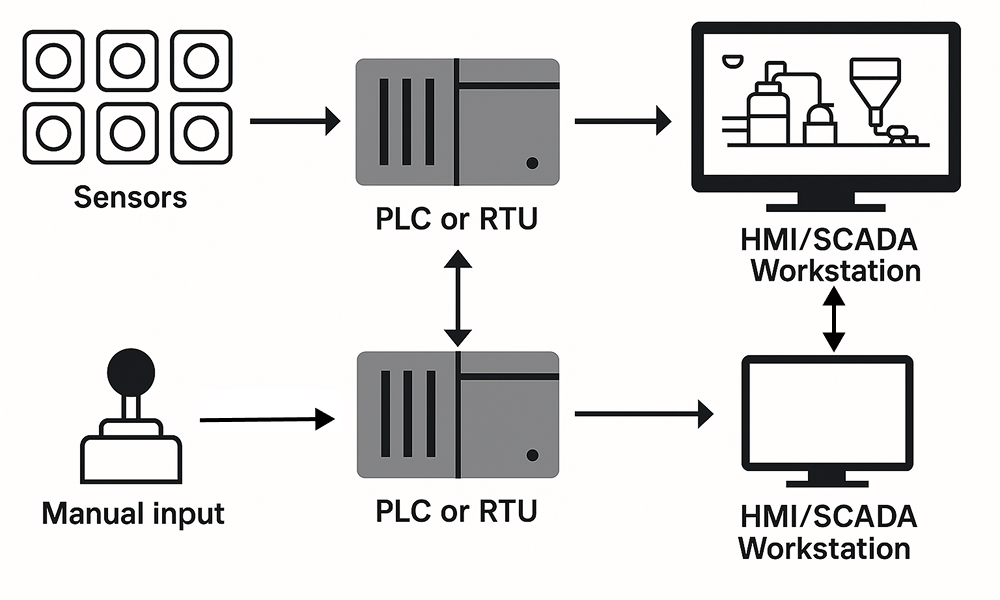
SCADA System Architecture: How It All Connects
A SCADA system is made up of different layers. Each layer has a role. Some collect data, others control machines and some help you see and manage it all.
Here’s how it works, layer by layer:
1. Field layer - The ground level
This is where the real-world action happens. It includes sensors, valves, motors, flow meters and other devices that measure or control physical processes.
2. Control layer - The local controllers
This layer involves PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers) and RTUs (Remote Terminal Units). They take input from the field devices and send it to the SCADA system. They also receive commands and control the equipment.
3. Communication layer - The link between devices
This layer connects controllers to the SCADA server and HMI. It uses protocols like Modbus, OPC-UA or Ethernet to transmit data in both directions, fast and reliably.
4. Supervisory layer - The SCADA server
This is the core of the system. It collects, processes and stores data. It manages alarms, logs events and creates reports. This server makes sure everything runs as expected.
5. HMI layer - The user interface
The HMI (Human-Machine Interface) is what you see on the screen. It shows live data, alarms and controls in a clear, visual format. Operators use it to monitor and manage the system.
Who Uses SCADA and Why?
SCADA is used by anyone who needs to monitor, control and manage industrial systems in real time:
Equipment Manufacturers
Machine manufacturers and OEMs use SCADA to view and control their systems. It helps them deliver smarter machines that are easier to support and integrate.
EPCs and System Integrators
EPC contractors and automation partners rely on SCADA to connect large systems across multiple devices, protocols and plants. It gives them one place to monitor everything.
Plant Engineers and Operators
SCADA helps on-site teams run day-to-day operations. From checking tank levels to responding to alarms, it gives them full control and reduces manual work.
Maintenance Teams
With SCADA logging data and events, maintenance teams can spot problems early, plan service and prevent downtime.
Managers and Decision-Makers
Through dashboards and reports, SCADA helps managers track performance, spot trends and make smarter decisions across sites or departments.
Industries where SCADA Systems are Most Commonly Used
SCADA is now a key part of many industries as they move toward automation, remote control and data-driven operations. Here are some of the top industries that rely on SCADA systems:
- Cement and minerals: To monitor and control processes like crushing, kiln and packing processes with better energy efficiency and uptime.
- Pharmaceuticals: For real-time monitoring of batch processes, cleanroom environments and compliance with FDA and GMP standards.
- Water and wastewater: To manage pump stations, tank levels and treatment processes remotely and reliably.
- Oil and gas: To supervise pipeline pressures, compressors and remote facilities across hazardous and wide areas.
- Renewable energy: To track solar and wind energy production, storage and load balancing across distributed sites.
- Food and beverage: For consistent product quality, automated recipe control and traceability.
- Smart buildings and infrastructure: For centralized control of HVAC, lighting and facility systems in airports, metros and campuses.
What is SCADA Programming?
SCADA programming involves creating the logic, scripts and configuration that allow a SCADA system to monitor, control and respond to industrial processes in real time.
It includes:
- Writing scripts or using built-in logic tools to define how the system reacts to events
- Setting up communication between the SCADA software and field devices like PLCs or RTUs
- Designing HMI screens that operators use to view data and control equipment
- Configuring alarms, trends, reports and data logging
- Managing user roles and security access
- Testing and validating the system’s behavior under different conditions
SCADA programming makes it easy for operators to see what’s happening, respond quickly, and get the right alerts and reports in real time. This helps industries reduce downtime, work faster and cut costs.
Popular SCADA software like Ignition, Siemens WinCC, Wonderware, Schneider Electric EcoStruxure and GE iFIX are widely used to build real-time monitoring and control systems across industries.
_Need expert support with SCADA programming and other industrial automation services?
Sedin Engineering helps OEMs, EPCs and automation teams build reliable SCADA systems and deliver end-to-end automation solutions, including PLC programming, HMI design, control panel engineering, and robotic simulation._
Benefits of SCADA Systems in Industrial Automation
1. Reduces downtime and equipment failure
SCADA helps you monitor systems in real time. It shows early signs of issues like overheating, low pressure or motor faults. Fixing problems early means fewer breakdowns and less unplanned downtime.
2. Improves operational efficiency
SCADA tracks how your equipment and processes perform. It helps spot delays, errors or slowdowns. This allows teams to act quickly and improve how things run.
3. Supports better decision-making
SCADA collects and stores important data. You can view reports, trends, and charts that make it easier to plan maintenance, increase output, or reduce waste.
4. Allows remote monitoring
With SCADA, you don’t need to be on-site to check system status. You can view and control processes from a remote location. This saves time and helps respond to issues faster.
5. Improves safety and compliance
SCADA watches process values all the time. If something goes beyond the safe range, it alerts the operator right away. It also stores records that help meet safety and audit requirements.
6. Helps reduce costs
SCADA reduces downtime, minimizes manual work and improves energy usage. Over time, these small gains can lead to big cost savings.
SCADA vs PLC vs HMI: Key Differences Explained
SCADA, PLCs, and HMIs are often used together in the same automation system, but each one serves a different role:
- PLC: Controls the machine in real time using programmed logic
- HMI: Provides the operator screen for monitoring and control
- SCADA: Supervises the overall system, collects data, and manages alarms across multiple machines
Here's a quick SCADA vs PLC vs HMI comparison to make it clear:
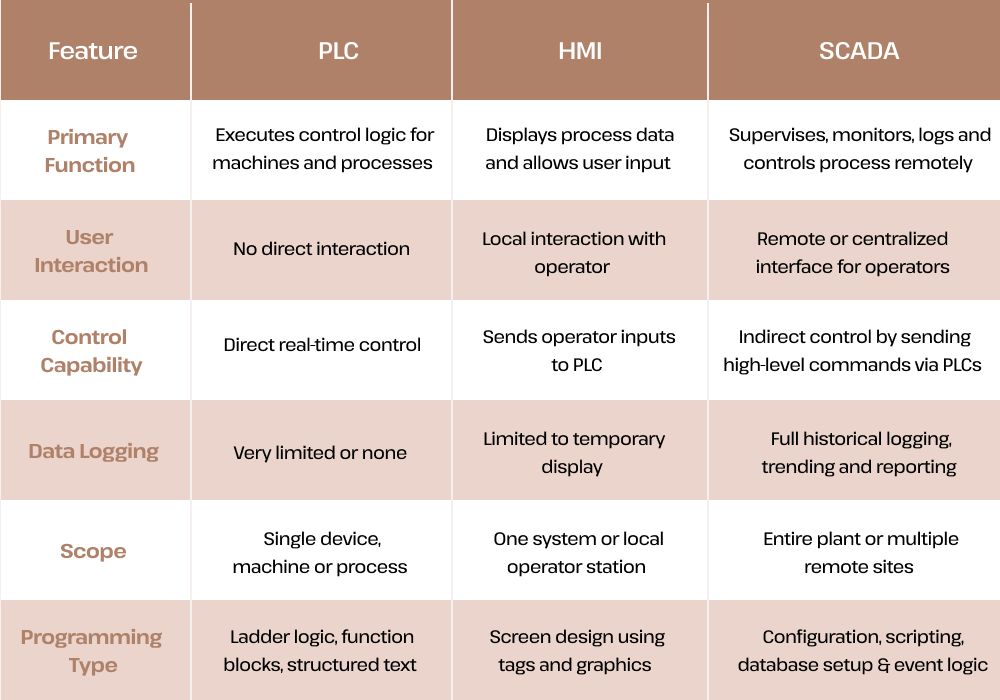
In simple terms,
- PLC handles control
- HMI handles interaction
- SCADA handles visibility, data and supervision
Together, they form the core of most modern industrial automation applications.
Do You Need SCADA Integration?
You’ve learnt what SCADA is, how it works, and why it’s needed. But do you actually need it in your setup?
Not every plant or system requires full SCADA integration right away. But as operations grow, data needs increase, and processes become more complex, having centralized visibility and control can make a big difference.
Here are a few signs that it might be the right time to invest in SCADA integration:
- You have multiple machines or PLCs but no centralised monitoring.
- Operators rely on manual checks or paper logs.
- You want real-time data visibility and control from one place.
- You're struggling with downtime, late alarms or lack of insights.
- You need better reporting for audits, compliance or optimization.
- Remote access or multi-site control is a priority.
If any of this sound familiar, SCADA integration could help you save time, reduce downtime and improve decision-making.
_We, at Sedin Engineering, design and programme SCADA systems tailored to your needs, whether it’s integrating with existing PLCs, building intuitive HMIs, or setting up full plant-wide monitoring.
Looking to modernize with SCADA or other industrial automation services? Let’s talk about a solution built for performance and growth._