Can solar and wind deliver power everywhere, all the time? The truth is: they can’t. But with Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS), it's possible. These systems are changing how energy is stored and used, ensuring a stable and reliable power supply even when renewables fluctuate.
In 2024, global energy storage installations have grown by more than 75%, and the momentum isn’t slowing down. According to BloombergNEF. total capacity is expected to reach 2 terawatts (7.3 terawatt-hours) by 2035 - almost eight times the level projected for 2025. This surge shows just how vital BESS has become to the world’s energy infrastructure.
For manufacturers and EPCs, this rapid growth also brings new engineering challenges. A BESS must be safe, scalable, and high-performing. And achieving this depends on the overall system design. From container layout and structural design to battery integration, thermal management, and electrical architecture, every factor affects safety and long-term reliability.
In this blog, we’ll break down the core components of a BESS, discuss key design considerations, and explain how a well-designed BESS can improve safety, efficiency, and overall system life – everything engineers and manufacturers need to create robust, high-performing energy storage systems.
What is a Battery Energy Storage System (BESS)?
A Battery Energy Storage System (BESS) is an integrated solution that stores electricity from the grid or renewable sources like solar and wind and releases it when demand rises or supply drops. This system helps stabilize the grid, improve energy efficiency, and ensure reliable power delivery.
BESS is typically built inside a containerized enclosure, which houses the batteries along with electrical, control, and cooling equipment. This enclosure protects the system from external conditions, maintains thermal balance, and ensures long-term safety and performance.
Common applications of Battery Energy Storage Systems
Battery Energy Storage Systems are used across many industries to make power supply more stable and efficient:
- Renewable energy plants – to store surplus solar or wind energy during peak generation and supply it back when production drops.
- Industrial facilities – to keep operations running by shaving peak loads and providing emergency backup during grid failures.
- Utilities – to regulate grid frequency regulation, manage energy flow, and support renewable power integration.
- Commercial buildings – to reduce demand charges, manage time-of-use rates, and integrate with on-site renewable or EV charging systems.
- Data centers – to provide uninterrupted power supply, minimize voltage fluctuations, and optimize load during peak demand hours.
Core components of a BESS
A Battery Energy Storage System (BESS) stores and delivers electrical energy using a combination of electrochemical, electrical, and mechanical subsystems. Each part has a specific role in ensuring efficiency, reliability, and safety.
- Battery modules
These are the primary energy storage units that hold electrical energy from the grid or renewable sources like solar and wind. Lithium-ion batteries are most widely used due to their high efficiency and long cycle life.
- Battery Management System (BMS)
BMS monitors and controls each battery cell’s voltage, current, temperature, state of charge (SoC), and state of health (SoH) to ensure safe and balanced operation. It ensures safe operation, prevents overcharging, and maintains balanced performance across all modules.
- Power Conversion System (PCS)
The PCS handles the bidirectional flow of power within the BESS. It converts DC from the batteries to AC for the grid or facility loads, and vice-versa during charging. It also manages critical parameters like voltage, frequency, and power factor to ensure stable and efficient operation.
- Thermal Management System
It maintains the temperature within safe operating limits through active or passive cooling systems. Effective thermal control extends battery life and prevents safety risks.
- Energy Management System (EMS)
It controls how the entire system operates. It decides when to charge, discharge, or store energy based on load demand, grid conditions, and operating strategy. It also provides supervisory functions such as optimal dispatch, load forecasting, data analytics, and grid interaction.
- BESS enclosure or container
It provides structural integrity and environmental protection. The BESS container design directly affects system safety, cooling performance, and ease of installation and maintenance.
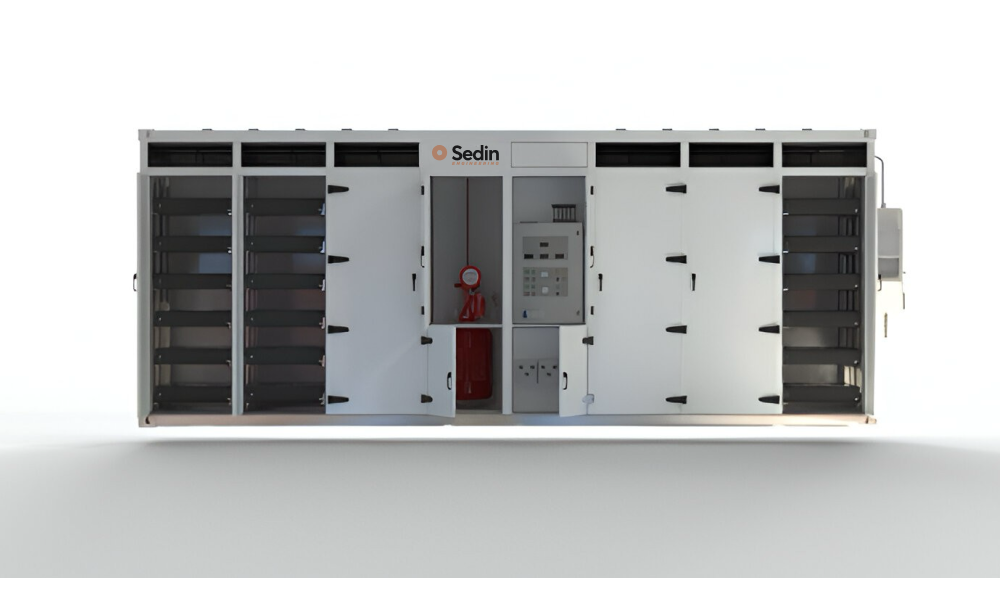

Key Design Considerations for BESS
Designing a BESS involves creating a system that ensures battery safety, efficiency, and reliability under real-world conditions. Every detail, from airflow and cooling to lifting points and maintenance access, directly affects system performance and lifespan. Here are some key factors to consider during BESS design:
1. Thermal management
Heat is one of the biggest challenges in battery storage. If the temperature inside the container isn’t controlled, it can shorten battery life or even create safety risks. That’s why airflow design, insulation, and cooling systems (like HVAC or liquid cooling) are important in any BESS design.
2. Structural strength and safety
The BESS container must do more than hold components. It has to protect them. The structure should handle outdoor exposure, mechanical loads, and extreme temperatures without compromising integrity. Using corrosion-resistant materials and meeting fire safety standards like UL 9540A ensures long-term reliability and compliance.
3. Space optimization
Internal space must be used efficiently to balance energy density and accessibility. An optimized layout provides enough space for safe cable routing and maintenance access. Modular designs also make it easier to scale capacity or replace components without redesigning the entire system.
4. Electrical and mechanical integration
A well-designed BESS keeps high-voltage and low-voltage sections clearly separated and easy to access. Conduit routing, grounding, and mounting provisions should all support smooth installation and safe operation. This minimizes rework during assembly or service.
5. Ventilation and fire suppression
Even the best batteries can fail if gases or heat aren’t properly managed. Effective venting systems, gas detection sensors, and fire suppression solutions (often gas-based) are crucial to reduce risks and protect both equipment and personnel.
6. Transport and maintenance access
Battery Energy Storage Systems must be designed for easy handling, installation, and servicing. Lifting points, service doors, and cable entry designs should be added to make transport, installation, and ongoing maintenance easier and faster, reducing project downtime and total cost.
BESS Design Standards and Global Compliance Requirements
While designing a BESS, following the right standards is just as important as good engineering. These standards ensure the system is safe, reliable, and ready for deployment across different regions.
IEC standards (Global / India / Europe)
- IEC 62619 – Safety requirements for lithium-ion cells and batteries
- IEC 62933 series – Design, testing, and grid integration guidelines for energy storage systems
- IEC 61427 – Performance testing for stationary storage
- IEC 61000 – Electromagnetic compatibility requirements
- IEC 60529 – IP ratings governing BESS enclosure protection levels
UL standards (United States)
- UL 9540 – Safety certification for complete BESS
- UL 9540A – Thermal runaway and fire propagation testing
- UL 1973 – Safety for stationary battery systems
- UL 1741 – Standards for inverters and power conversion equipment
NFPA standards (US Fire Safety)
- NFPA 855 – Installation requirements for energy storage systems
- NFPA 70 / NEC – Electrical safety and wiring rules for ESS
Indian regulations
- Alignment with major IEC standards
- CEA safety regulations for battery installations
- DISCOM interconnection and grid compliance requirements
Complying with these standards ensures that BESS systems operate safely, integrate smoothly with the grid, and deliver long-term reliability across different regions and applications.
Benefits of a Well-Designed BESS
Design plays a direct role in how well a battery energy storage system performs in the field. BESS designed for safety, efficiency, and manufacturability (DFM) run reliably, install faster, and are easier to maintain. Here’s how a well-designed BESS adds real value to manufacturers:
1. Improved safety and reliability
Thermal events and electrical faults remain two of the biggest risks in battery storage. A structurally sound BESS with fire-rated panels, gas detection, and pressure relief design minimizes those risks. This protects both equipment and people while meeting standards like UL 9540A.
2. Extended battery life
Battery performance depends heavily on temperature consistency. BESS designed with even airflow and optimized HVAC placement prevents hotspots, helping maintain capacity and reduce degradation over thousands of cycles.
3. Easier maintenance and upgrades
When access panels, cabling routes, and component placement are planned from the start, maintenance time drops significantly. Field teams spend less time troubleshooting and more time keeping systems running, which is a major advantage for large-scale deployments.
4. Higher system efficiency
Energy losses often occur due to poor layout or long power paths. Optimized electrical design, shorter cable runs, and efficient cooling flow reduce conversion losses and improve efficiency. This is another critical factor for ROI and performance guarantees.
5. Faster deployment and scalability
Pre-engineered BESS can reduce on-site installation time by up to 30%. Modular layouts also let EPCs scale storage capacity without redesigning the entire infrastructure, making future upgrades simpler and more cost-effective.
Trends Driving BESS Adoption
Now that the benefits of well-designed storage systems are clear, the next question is: what’s driving the growing demand? The move toward cleaner and more reliable power is changing how manufacturers, EPCs, and utilities plan their energy systems. Here are the key trends pushing BESS adoption across industries:
1. Rapid growth in renewable energy
The share of renewable resources in global power generation continues to rise, but solar and wind come with intermittency challenges. BESS helps balance this by storing extra energy and supplying it during peak demand. It also supports the grid through peak shaving, energy shifting, smoothing, and frequency/voltage stability.
2. Energy security for data centers
Industrial facilities like data centers need uninterrupted power to keep critical operations running smoothly. BESS for data centers provides fast backup, stabilizes power during fluctuations, and pairs effectively with diesel or hybrid systems to maximize reliability and uptime.
3. Grid infrastructure limitations
Aging grid networks in many regions can’t expand fast enough to match rising energy demand. BESS helps bridge this gap by providing localized power support, reducing peak loads, and delaying the need for expensive grid upgrades.
4. Falling battery costs
Lithium-ion battery prices have dropped over 80% in the last decade, making BESS more economically viable for both utility-scale and commercial projects. This cost reduction is opening opportunities for wider deployment across sectors.
5. Policy and regulatory push
Governments in the USA, Europe and the Middle East are setting aggressive renewable energy targets, supported by tax incentives and subsidies for storage integration. Clearer grid interconnection standards are also speeding up project approvals.
5. Shift toward mobility & portable power
Manufacturers and EPCs are moving toward mobile BESS solutions that simplify deployment and maintenance. They can be used for:
- Temporary power at construction sites
- EV charging hubs in remote or high-demand locations
- Disaster relief and emergency response
- Defense, mining, and other off-grid operations
Let’s Design Safer, Smarter and Scalable Battery Energy Storage Systems
In battery energy storage, design directly impacts system performance, safety, and long-term reliability. At Sedin Engineering, we transform complex BESS requirements into practical, high-performing solutions through our product design engineering services. Our expertise covers:
- Advanced BESS enclosure design: Fire-rated containers, airflow optimization, and structural analysis for wind and seismic loads
- Electrical & harness engineering: Fault-tolerant architecture, HV cable routing, protection coordination, and UL/IEC-compliant harnesses
- Thermal & safety engineering: Thermal component support, fire detection, and suppression systems
- Modular & serviceable architecture: Hot-swappable units, plug-and-play racks, and rapid maintenance with no downtime
- Capacity scaling: Designs up to 7.5 MWh, modular layouts for containerized, skid-based, or custom industrial setups
By combining global standards compliance with practical, scalable designs, we help integrators reduce engineering risk and accelerate development cycles. Every BESS we design delivers reliable, safe performance for real-world deployment.
Want a BESS design that performs reliably and meets global standards? Contact us to bring your next energy storage system project to life.