To address the challenges of designing an efficient automation line for clip assembly, we conducted in-depth research into design aspects to meet the client’s requirements and ensure smooth integration into their production process.
Our solution optimized the design of the inline slat conveyor, roller conveyor, and pick-and-place assembly. Here's a detailed breakdown of each part:
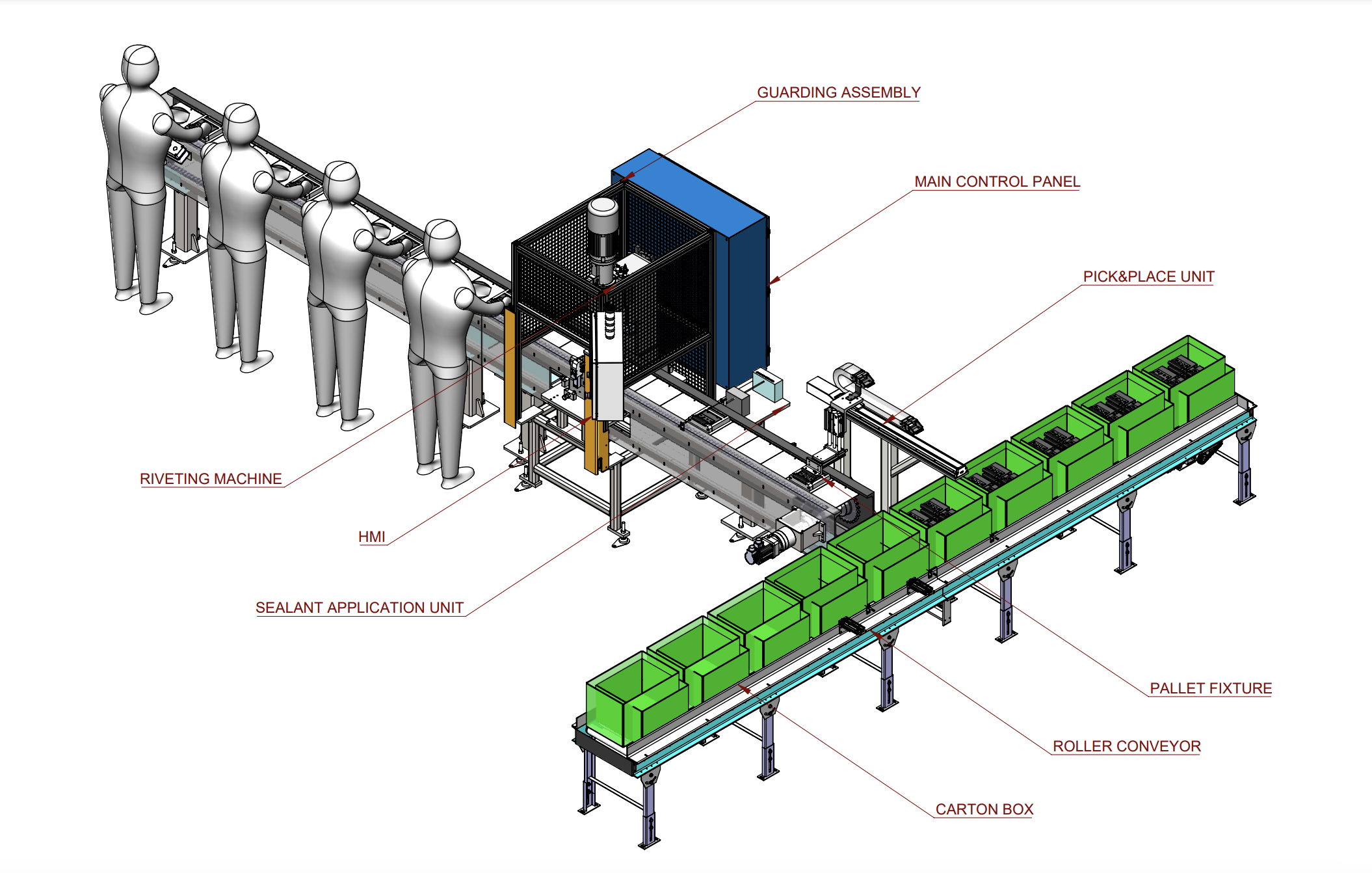
Inline Slat Conveyor Design
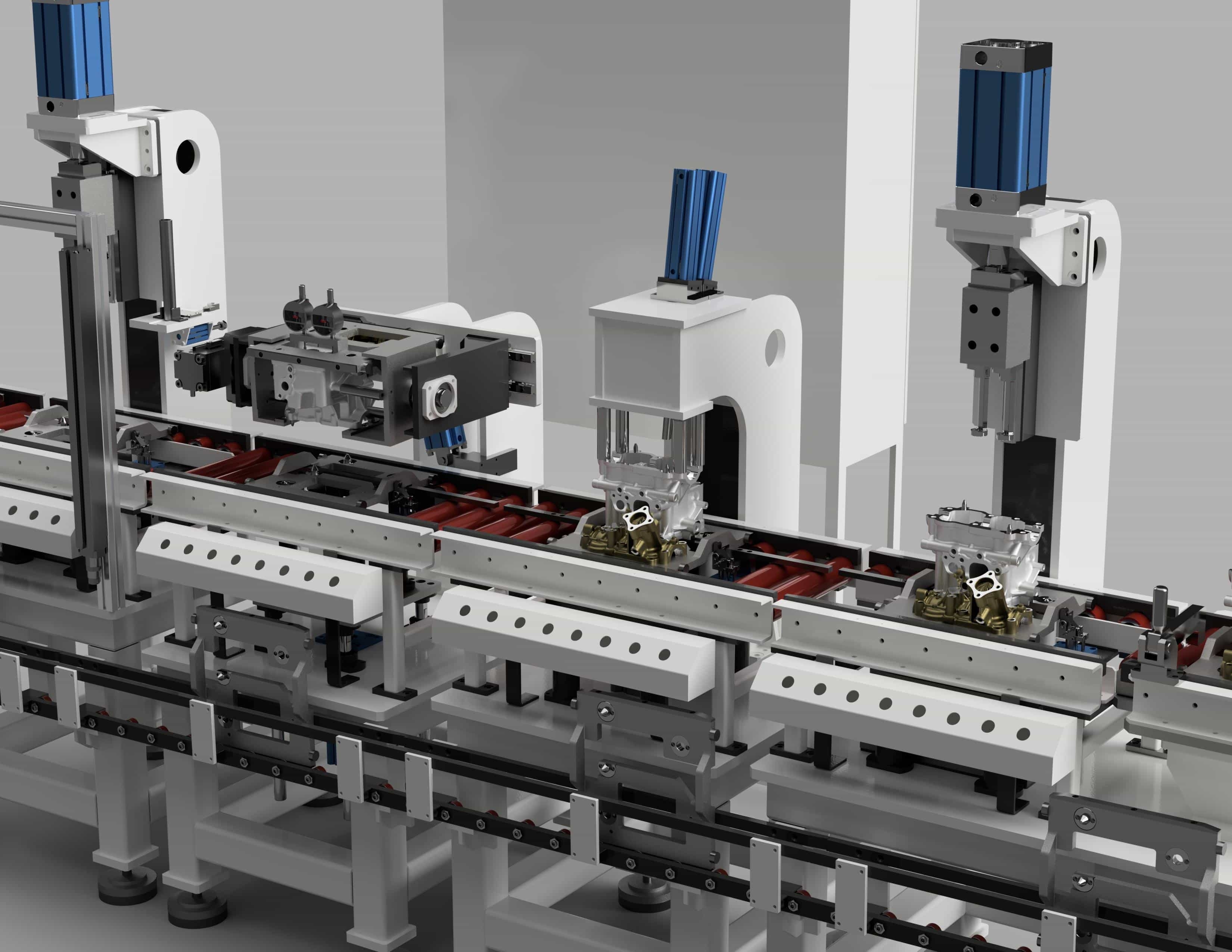
- After several technical discussions between the designers and automation engineers, we leveraged our SolidWorks expertise to design an efficient inline slat conveyor. The conveyor included seven stations: four for manual operators, the fifth for riveting, the sixth for sealant application, and the last for unloading components.
- We designed pallets and fixtures to accommodate different component variants without the need for setup changes. Poka-yoke technique was used to ensure error-proof handling.
- We integrated a servo system to drive the slat conveyor, utilizing chains and sprockets, supported by bearings, tensioning, and guides. The pallets were fastened to the chains with A-type links to ensure secure transportation of components.
- At the riveting station, we used a pneumatic clamp to securely hold the pallet and fixture while riveting, with extra support underneath the pallet to keep everything steady during operation. We also added sensors at both the riveting and sealant stations to ensure the components are always in the right position.
Pick and Place Assembly Design
- We designed a pick-and-place unit to transfer the finished component from the inline slat conveyor to the carton box on the roller conveyor. The unit included a servo-driven linear actuator, vertical and horizontal pneumatic actuators and suction cups.
- The vertical actuator with suction cups would pick the component from the fixture on the slat conveyor and the horizontal actuator would transfer it to the roller conveyor, placing it into carton boxes at different positions. To ensure everything aligned correctly, we used vision sensors for accurate placement.
Roller Conveyor Design
- The roller conveyor was designed to carry empty and components-filled carton boxes to the next stage of the process. It is driven by rollers with built-in sprockets, connected to a geared motor with a variable frequency drive to control the speed.
- We integrated pneumatic stoppers, a singling system, a pusher, and sensors to the roller conveyor. The pusher and stopper ensured proper placement of components, while the singling system prevented empty boxes from colliding. Sensors, placed at key points, monitored the movement of carton boxes. They would activate end stoppers to prevent the boxes from falling off the conveyor.
- The design ensured that the roller conveyor supported seamless integration with other automation systems and machinery, improving the overall productivity.
- We also ensured that all safety and ergonomic standards were met according to the client’s requirements.
The designs were developed with a focus on reliability and efficiency, taking into account the findings from the Design Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (DFMEA) to address potential risks and enhance system performance.
With the help of Sedin’s cost-effective and state-of-the-art industrial automation solutions, the entire cell was able to work continuously without any hassles, thereby increasing the productivity.